Farrinstitute is reader-supported. We may receive commissions on purchases made through links on our site.
Testosterone is an important hormone for women and plays a key role in regulating bone density, muscle mass, sex drive (libido), insulin levels, and overall general health and fitness.
Excess testosterone brings about several unwanted physical changes as well as a degradation in overall health.
Women produce testosterone and free testosterone just like men, but in smaller amounts [1]. The natural levels of testosterone in a woman will vary with age–peak production is just after birth and at puberty [2]. Thereafter, levels will slowly drop and by the time a woman is in her 40’s, her free testosterone levels will have halved.
Here’s an example of normal testosterone levels in females from birth to 19 years:
Any sort of hormone imbalances, either high or low testosterone may cause health issues of varying significance.
Read on to learn more about testosterone levels by age.
Long-term elevated testosterone may exhibit a number of symptoms. It may affect your health, appearance or both [3].
Elevated testosterone (androgen) levels can affect a range of body tissues and typically cause women to express what would be thought of as stereotypically male traits.
Testosterone and other androgens work slowly. Their effects are not felt like, say, ibuprofen, which is almost immediate. For the effects listed below, it is necessary to have raised testosterone levels for months.
Too much testosterone may cause post-pubescent acne which can be quite severe and disfiguring. It is most notable on the face, chest and back.
One of the symptoms of high testosterone levels is a condition known as hirsutism. The hair growth will generally be coarser and darker than normal. It will grow on the face, typically the upper lip, the chest, and back.
Testosterone is often used by bodybuilders to gain muscle mass and increase bone density. Having elevated testosterone will certainly result in weight gain, a larger frame, and ‘bulking up.’
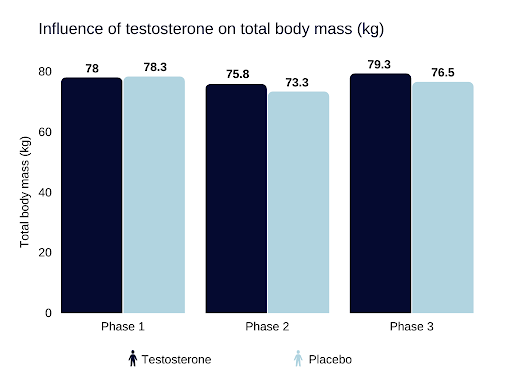
The testosterone group showed a more significant increase in total body mass compared to the placebo group
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6711889/
Higher free testosterone levels will, over time, result in a reduction in breast size. You can also see this effect in female bodybuilders who use androgens and are interested in extreme muscle gain.
Elevated testosterone levels can result in morphological changes to the body. The larynx (voice box) and vocal cords will change shape, resulting in a lower voice.
High testosterone production is linked to male pattern baldness or androgenic alopecia (hair loss) in women. This is usually seen as a receding hairline and hair loss on the crown of the head.
A result of high testosterone levels is a prominent clitoris. The penis is an outgrowth of cells that, in females, become the clitoris. The result is an enlarged clitoris where there is a hormone imbalance.
Any derangement of the sexual hormones can affect fertility. The contraceptive pill is exactly this, a change in the female hormones.
Excessive androgens, such as testosterone, over a length of time, can lead to a suppression of egg maturation and therefore infertility.
Once the normal hormonal balance is restored, ovulation and fertility should return to normal.
One symptom of high testosterone in women can be a loss of libido and a reduction in sexual gratification.
This is only a temporary effect of elevated testosterone in women and should quickly return to normal when testosterone levels are back on track.
Any hormonal imbalance can cause irregular periods. Either high testosterone or low testosterone in women can upset a regular cycle.
Hormonal birth control works by creating an artificial baseline for the hormone level and stops or reduces periods.
When the testosterone imbalance is addressed, the menstrual cycle should return to its previous normal.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is commonly caused by abnormal levels of testosterone. Women with PCOS show a range of the symptoms detailed above [4].
Your healthcare provider will run a number of tests, such as a pelvic exam, a physical, an ultrasound, and blood tests.
Your doctor may recommend birth control pills. They will quickly help lower androgen production, which will help alleviate the symptoms once normal testosterone levels are achieved.
If polycystic ovary syndrome is caused by raised hormone levels, your doctor may prescribe diabetes medications to help balance your blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity. Reducing insulin resistance and blood sugar control can help women with PCOS [15].
Another trigger of polycystic ovary syndrome is obesity. Your health care provider will likely suggest a regime of healthy eating and exercise.
Dietary changes can alleviate the symptoms and can also help reduce insulin resistance. This can lower blood glucose and help you ovulate.
Testosterone is an important hormone but if you suspect something is amiss, not just polycystic ovarian syndrome, you should always consult your physician.
There are various treatment options available for women who are dealing with raised testosterone levels, however, the right treatment for you depends on the cause.
Treatment options generally include certain medications or lifestyle changes, which we will get more into below.
If medical treatment isn’t up your alley, diet changes might just be all you need to lower your testosterone.
Soya beans contain phytoestrogens. These are compounds found in certain plants that mimic the effect of estrogen in the body.
One of the effects of high estrogen in the body is it reduces testosterone levels. Some studies have suggested good results whereas others have been less promising [6][7].
Cow’s milk naturally contains small amounts of estrogen, progesterone and other hormones–it may also contain synthetic hormones. The feed for cows can also contain soy and soy-based products.
This can help to decrease testosterone slightly.
Green tea is known for its many health benefits. Studies have now shown that it may also be able to lower total testosterone levels in the body [8].
Green tea prevents the formation of DHT, a hormone formed from testosterone. DHT has the same effect as testosterone but is far stronger.
Marjoram is a common herb known for its health benefits and anecdotal ability to restore hormonal balance and to regulate the menstrual cycle.
Women in a randomized controlled trial received marjoram for a month. Insulin sensitivity was improved and blood sugar levels lowered compared to the cohort taking the placebo tea [9].
Overall this resulted in low testosterone compared to women with PCOS.
A study showed that this species of Japanese mushroom was the most effective of the 20 tested in reducing 5-alpha-reductase [10]. This enzyme converts testosterone into DHT.
There have been a number of clinical trials with spearmint and peppermint teas that have demonstrated a lowering of testosterone in women [11].
In one trial the spearmint tea group showed lower testosterone levels compared to the placebo tea group.
Limited studies have been done with almonds and walnuts that show a decrease in testosterone levels in women.
Tests showed that the sample group of women displayed an increase in sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) by around 14% [12].
Sex hormone-binding globulin is a type of protein found in the blood that preferentially binds to testosterone, lowering the amount available in circulation.
There is slight evidence suggesting that some fish oils may be beneficial to health. In women with PCOS, omega-3 oil has been shown to lower testosterone levels in women [13].
Along with the foods mentioned above, there are different supplements and vitamins that could help you lower testosterone levels in your body.
A study showed that taking licorice supplements can reduce testosterone in healthy women during their period [15].
A study consisting of a single woman with PCOS showed reduced total and free testosterone. The dose of flaxseed tested was 30 grams per day. During and after the trial, the patient also reported a decrease in overall hirsutism [16]. A study consisting of a single individual isn’t statistically sound, but if further study is carried out, it may be one to monitor.
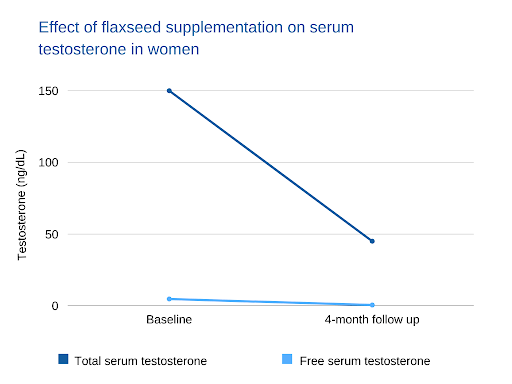
Supplementing with flaxseed showed to lower serum testosterone in four months
Source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19789727/
The evidence isn’t really definitive on flaxseed supplementation, but as part of an overall total body approach, it may have some efficacy.
If all else fails, or your case is more severe, there are medications that can help to lower testosterone.
The standard hormonal contraceptive pill (with estrogen) is effective at regulating hormonal imbalances and regulating menstrual cycles.
There is a large selection of prescription medications that can be very effective at reducing total testosterone levels. Depending on the presentation and/or severity of the condition your doctor can advise you of the best course of treatment.
Common medications include the following:
These medications are commonly known as anti-androgens or steroidal anti-androgens, and can be used by men, women and those in gender transition.
These drugs may reduce the symptoms of your high testosterone but they do not address the underlying cause of the issue.
High levels of testosterone are less of a problem in men, far less than low testosterone levels are.
Regulation can be quite easy with diet and exercise. The food sources listed above, typically what people would associate with healthy eating, would help. Lots of polyunsaturated fatty acids, fresh fruit, and vegetables for example.
The range of medication listed above is broadly suited to men if the androgens are at clinically significant levels.
If issues persist, visit your health care professional.
Yes, there are. Any of the supplements listed above would work just as well with men. There are no gender-specific treatments, with the exception of the contraceptive pill.
Here is a breakdown of some of the most commonly asked questions regarding high testosterone in women and some of the treatments involved.
Long-term raised levels of testosterone will have a number of wide-ranging effects such as physical/cosmetic changes in the body or poor heart health and heart disease.
If the underlying reason is a metabolic disorder or PCOS then this needs to be the focus of the treatment. Your doctor will assess you and devise a treatment regime, usually, this can be lifestyle changes or medications.
If you have noted any unwanted changes in your body then high levels of testosterone may be to blame.
Your doctor will highlight any issues but there are many positive steps you can take to lower high insulin and lower high testosterone.
The effects of high testosterone take a while to manifest. Likewise, the recovery and reset may also take months. With the proper care and attention, you will be fine in no time.