Farrinstitute is reader-supported. We may receive commissions on purchases made through links on our site.
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone that plays a vital role in male and female health, and it is one of the key anabolic hormones.
If you feel you lack energy, have a low libido, or have issues with sexual function, then low testosterone could be an issue. For women, the signs also include symptoms of osteoporosis or hair loss.
In this article, we will show you how to increase your testosterone levels naturally and healthily. With just a few changes to your diet, you can find a quick fix to raise low testosterone and give your hormone levels the kick that you need for that extra spark and energy you may be missing.
Here is a quick overview of the top 15 foods that act as a natural testosterone booster:
We know testosterone is key to our health [1]. Wondering how to increase testosterone? One of the quickest and easiest ways anyone can take personal control over their hormone levels is to adopt healthy habits.
By making a few choices about what you eat, you can raise your testosterone levels naturally. We have compiled a list of foods to help you do just that.
Increasing your vitamin D intake is an excellent way to boost testosterone levels [2]. D vitamins play an important role in the manufacture of testosterone in your body.
Fortified milk has a raised vitamin D content and should be part of your diet. It is a quick and easy dietary change to make, one with certain benefits.
Oysters are rich in zinc—in fact, they contain more zinc than any other food. Zinc just happens to be an essential nutrient in the manufacture of testosterone [3].
Making sure that you have a diet rich in the minerals needed to produce testosterone is a surefire way to help with testosterone increases.
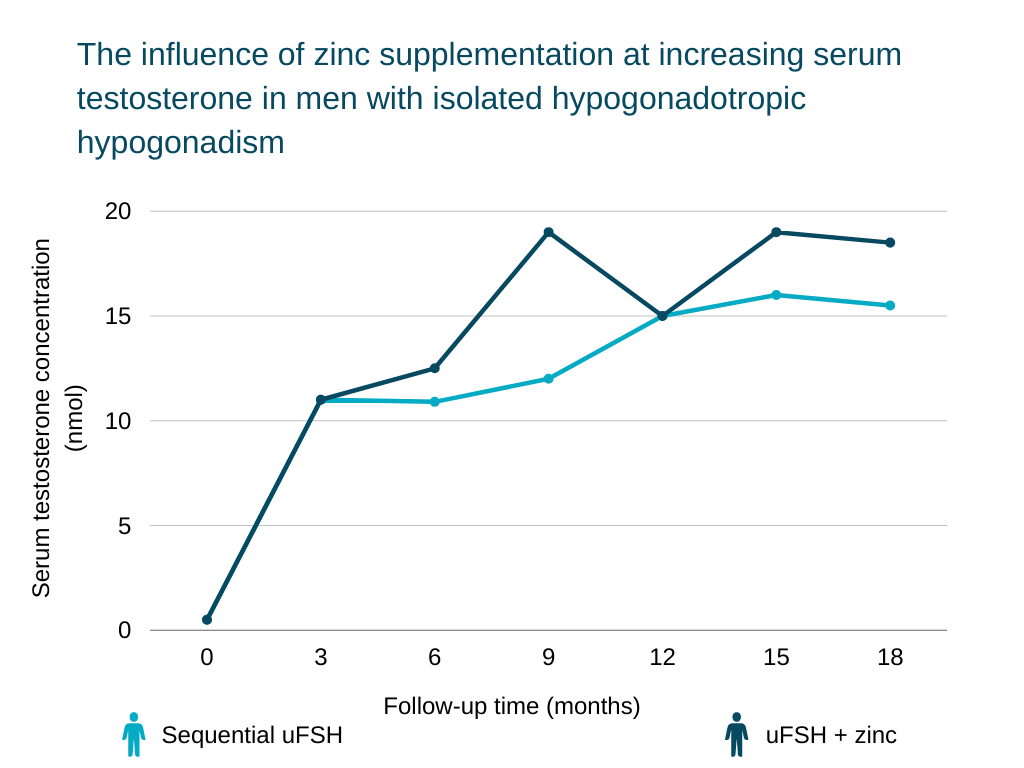
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5427781/
Shellfish are rich in trace elements such as zinc and magnesium and have been found to significantly boost T levels [4]. An easy and effective way to help your body make all the testosterone it needs is to ensure it is well supplied with all the building blocks it needs.
Fatty fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These long-chain fatty acids have long been known to have many health benefits.
Good sources of fatty acids are:
A medically reviewed study from 2017 showed that serum testosterone levels in healthy young men were raised with fatty acid intake. It also showed better reproductive health and healthier sperm (motility and activity) [5].
Tuna is rich in vitamin D, protein, trace minerals, and micronutrients. A single serving of tuna can fulfill all your daily dietary needs of vitamin D [6].
We know that this vitamin is key in the production of sex hormones, and as such, is a good addition to any healthy diet [2].
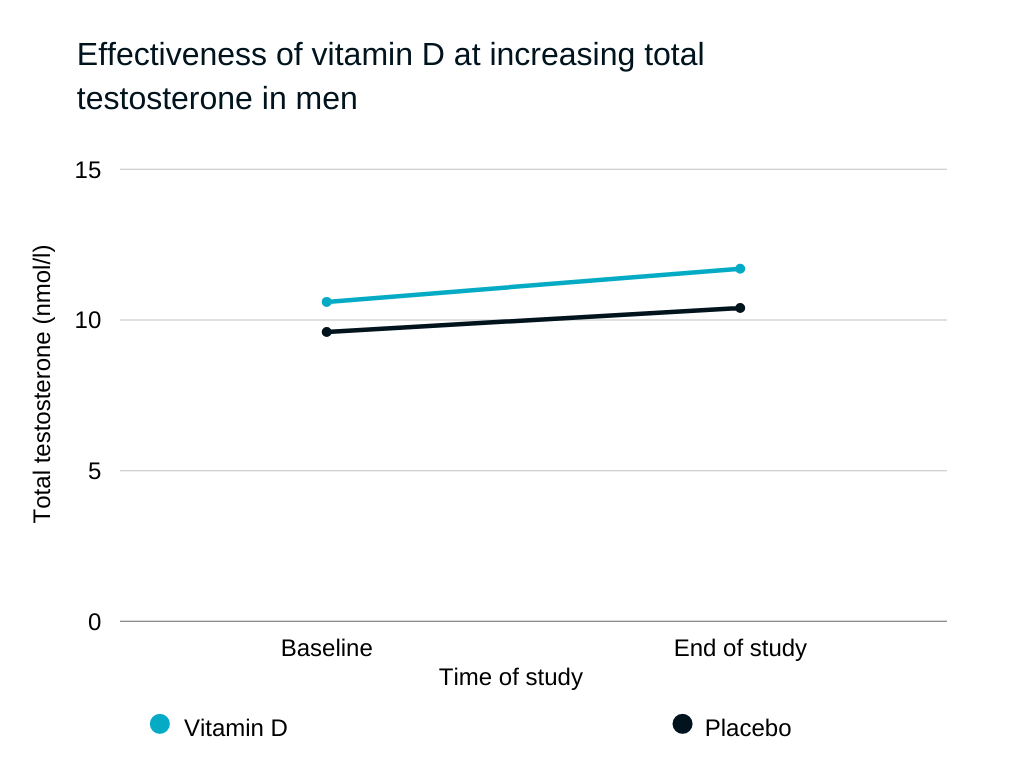
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6842386/
Egg yolks are a great source of D vitamins. They are also key to maintaining healthy cholesterol levels, another building block of many hormones [2].
For normal healthy males, eating one boiled or scrambled egg a day poses no risk. Your health provider can provide medical advice and a cholesterol check if you are concerned.
Olive oil is a key component in the Mediterranean diet, long-established as one of the healthiest diets. As such, it is a good starting point for a good dietary choice.
In addition to the benefits of a healthy diet, small-scale studies have shown that in young healthy men, extra virgin olive oil may help raise testosterone levels [7].
If you have concerns over high cholesterol levels and/or eating beef or eggs, then fortified cereals are a great method of zinc and vitamin D supplementation to your diet [2].
If you have a plant-centered diet, then fortified plant milk is an excellent source of essential vitamins and minerals.
We know that vitamin D plays a role in testosterone production, so a tall, chilled glass of the milk of your choice is a great way to add extra D vitamins to your diet [2].
Onions are a great staple food, the cornerstone of many tasty dishes. They are known to have a range of health benefits, but studies show they may also help raise testosterone production by boosting luteinizing hormone [8].
We all know that leafy greens should be part of a healthy diet. Spinach is a great choice, as is chard, kale, and a number of other green veggies.
All are rich in magnesium (among other minerals). Studies indicate that consuming higher levels of magnesium can lift low testosterone levels [9].
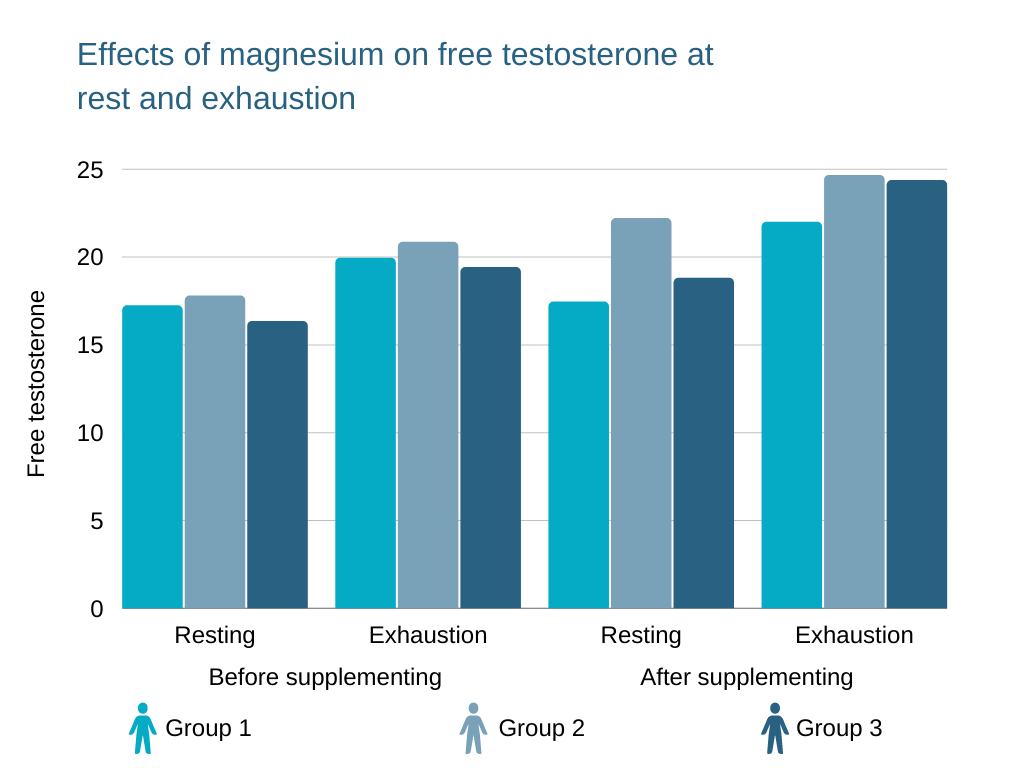
Source: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12011-010-8676-3
Beans may not be at the top of many people’s lists when it comes to boosting reproductive hormones. They are usually known for their other, more effervescent effects.
Beans (lentils, chickpeas, and legumes in general) are key to a plant-based healthy diet. They are full of protein, carbs, and both zinc and magnesium.
We have already discussed the benefits of boosting the two essential minerals, and eating plenty of beans is a cheap, healthy, and tasty way to up your T levels [3] [4].
Beef products, such as beef liver and ground beef, are rich in protein, huge amounts of micronutrients, and a wide range of vitamins [6].
The term “superfood” is used a lot in the media, but for male sex hormone production, this really is not a misnomer.
As part of a balanced diet, lean beef is nutritionally dense, healthy in the right quantities, and provides a huge dietary boost that leads to increased levels of testosterone [10].
Pomegranate is an aromatase inhibitor, which prevents testosterone from converting to estrogen. A medically reviewed study of 60 healthy men and women that drank pure pomegranate juice showed promising results after only 14 days [11].
The participants had, on average, a 24% increase in their testosterone level. In addition, they reported lower stress levels and a feeling of wellbeing, both key to helping to raise testosterone.
Ginger has been used for thousands of years as a tonic for better blood flow and as a medicine for nausea, digestion, and colds and flu. Current research has suggested that it may well have testosterone-boosting properties in addition to the aforementioned benefits.
A study in rats showed an increase in both testosterone levels and antioxidant levels after just 30 days of ginger intake [12].
A medically reviewed study pointed to a 17.7% increase in testosterone levels and a boost to sperm count and quality (motility and viability) after using a daily ginger supplement [13].
Can you hit two birds with one stone? Here is a quick checklist of foods that can do that for you by increasing testosterone and lowering estrogen:
This is an important group of foods, including broccoli, cauliflower, Brussel sprouts, kale, turnips, and cabbage. Not only are they healthy, they also boost testosterone.
This group is high in indole-3 carbinol and diindolylmethane (DIM). These are an essential addition to the male diet as they are aromatase inhibitors. This slows the production of estrogen and makes testosterone regulation easier in men [14].
An added bonus is that eating cruciferous vegetables may lower the risk of prostate cancer, a common problem in older men [15].
Curcumin is a main compound present in turmeric, known for its anti-inflammatory effects. Studies have shown that it can raise testosterone when given in large doses [16].
A separate study from 2013 indicated that it might have an effect on lowering estrogen, although this was only in a laboratory, so more work here is needed [17].
Green tea is a powerful aromatase inhibitor, and studies show that it can lower estrogen levels [18].
As noted above, fortified plant milks (such as soy milk) can be an easy and valuable way to increase vitamin D levels and boost testosterone naturally. Read more on if soy is bad for men here.
There are a number of foods that may have the ability to lower testosterone levels or lower testosterone production, such as:
Processed foods are a problem when it comes to reproductive hormones, as are trans fats. A 2016 study showed that trans fats can adversely affect testosterone levels [19].
A 2018 study showed that high levels of sugar-sweetened beverages in a diet resulted in a lowering of testosterone levels. Research also showed that having a BMI constantly over 25 was a risk factor too [20].
Human and animal testing has demonstrated a drop of up to 26% in testosterone levels with licorice consumption. This treat may be one to drop if your T levels are too low [21].
A recent study showed that a diet rich in cooking oils (fried foods) was linked to lower testosterone levels. This could be linked to high BMI, but it is worth cutting down if you want to keep your testosterone level in the healthy range [22].
This isn’t strictly a food, but if there is one single thing you can cut out of your diet to boost your T levels, it should be alcohol.
Alcohol is the one medically proven substance that has the most dramatic effect on testosterone levels. Regular or heavy drinkers have a range of medical issues, not least of those being shrunken testes, chronic liver issues, and low testosterone [23].
There are a number of non-dietary ways to naturally raise your testosterone levels:
You can cultivate a number of healthy habits, and a few small changes can produce a range of beneficial changes to testosterone levels.
If you are looking to boost testosterone naturally, then a healthy balanced diet is always a good idea. Ensuring that all food groups are represented and in their correct proportions is sure to boost your testosterone.
Choosing your foods with a little care can have a big positive impact on testosterone production.
An excellent way to boost testosterone naturally is to cut down on alcohol. Excessive drinking will have an adverse effect on your testosterone levels leading to issues such as erectile dysfunction [23].
A good way to increase testosterone naturally is with regular exercise. Resistance training has been shown to have a number of health benefits other than as a natural testosterone booster [24].
Medically reviewed papers have shown that an increase in muscle mass can raise blood flow, increase bone health, raise the number of red blood cells, and lower BMI.
Losing weight will also help, as having a high BMI can lead to insulin resistance. This can, in turn, lead to low T levels [25].
Raised cortisol levels are the enemy of the production of key hormones. Many studies have demonstrated that chronic stress leads to lower free testosterone and lower serum testosterone levels [26].
A popular way to raise low testosterone is with supplements and testosterone boosters. They are readily available over the counter in health stores or online.
Testosterone supplements or even testosterone replacement therapy can be used to quickly address erectile dysfunction, improve sexual function, raise sperm count, and improve male fertility.
The supplements contain a mix of essential nutrients, vitamins, and herbal supplements to help boost T production. The most effective are Testogen, Test RX, and TestoPrime.

We will run through some of the most common questions about foods that increase testosterone.
Foods that are high in zinc, D vitamins, and omega 3 fatty acids are the best to boost testosterone levels. These include oysters, pomegranates, ginger, egg yolks, and fatty fish.
Exercise that leads to a boost in muscle mass is ideal. High-intensity workouts have been clinically proven to raise free testosterone levels [24].
There is no definitive proof that caffeine can change testosterone levels. A study with around 20 healthy young men was inconclusive [27]. Further research with larger sample sizes is needed for meaningful data.
As men age, testosterone levels naturally fall. From the age of 30 years onwards, there is roughly a 1% drop in overall testosterone levels each year [1].
As this occurs, estrogen levels will naturally rise slightly, but the rise and fall are not clearly linked. There is a hormone called aromatase which can convert testosterone into estradiol, an estrogen precursor.
The conversion from testosterone to estradiol is not thought to be a significant factor in low testosterone levels.
If you have problems with testosterone levels or you just want to give yourself a natural boost, there are many options open to you.
A change in diet, lifestyle, and a new exercise regime can make a huge change. You can make a conscious choice to alter your diet, actively selecting a range of beneficial foods.
Take control of your weight and lose weight if necessary. Having a long-term BMI of over 25 will lead to a lowering of your testosterone levels and a higher risk of associated issues.
A third viable option is to choose one of a range of natural testosterone boosters. We recommend Testogen, Test RX, and TestoPrime as the three market leaders.