Farrinstitute is reader-supported. We may receive commissions on purchases made through links on our site.
Dealing with mood changes, poor concentration and even erectile dysfunction is no way to live. Truth is, these symptoms point to a bigger problem than age or a poor diet—they’re telltale signs of a testosterone deficiency.
Testosterone cypionate is a self-injectable solution your doctor might prescribe you in case of low testosterone. We’re going to take you through exactly what this drug is, how it may help you and potential side effects.
So, let’s get to it.
Testosterone Cypionate (TC) is a drug that mimics the effects of the body’s testosterone. It is known as an anabolic steroid (AAS). You may have heard of them in relation to sport or body building, where many are banned [1].
TC and its derivatives, such as testosterone enanthate are a Schedule III controlled substance. This means it has a moderate abuse potential and should be prescribed and used with care [2].
Hormones are one of the most powerful chemicals made by the human body. As you can imagine, taking a drug that mirrors the effect of these chemicals can come with great risk.
If your free testosterone levels are too low for some reason your doctor may prescribe testosterone cypionate to replace lost hormone function or boost low levels [3].
In addition to obesity, damage from trauma, alcoholism or mumps, delayed puberty and hypopituitarism also can cause low testosterone levels. Genetic diseases such as Klinefelter syndrome, myotonic dystrophy and Kallmann Syndrome may lead to lower than normal production.
Male hormones regulate or maintain male primary and secondary sexual traits. Androgens (exogenous androgens are ones produced by the body) are produced in the testes, the adrenal gland, and the ovaries. Women also produce androgens, but at much lower levels than men.
Men (or boys) that do not produce enough testosterone are known as hypogonadal males [4]. If you have reduced levels of testosterone as a child, you may suffer from delayed puberty [5]. This may, in turn, result in compromised adult stature.
You can suffer from reduced free testosterone levels for a number of reasons. It may be due to injury or radiation exposure, a number of metabolic disorders, or could be due to a genetic disorder.
People who suffer from delayed puberty show underdeveloped male sex organs, increased bone age, and other hormonal imbalances.
Testosterone replacement therapy is a single or group of medical interventions seeking the augmentation or full replacement of the body’s testosterone. Your doctor will choose the delivery system that is best for you, typically intramuscular injections, they may also offer a skin patch, oral doses or subcutaneous pellets.
There are a number of drugs that can be prescribed, again your physician will make this choice based on the best fit for you.
The drugs typically prescribed all mimic the action of testosterone, usually testosterone esters such as testosterone enanthate, testosterone undecanoate, and testosterone propionate [6]. All are sold under differing generic/brand names.
See our article on Testosterone Replacement Therapy.
Testosterone cypionate, also known as Depo-Testosterone is a drug that mimics the action of endogenous testosterone. It triggers all the associated effects of testosterone. TC can increase bone mass and density, trigger secondary male characteristics, and it can lead to a build-up in muscle mass.
Testosterone and therefore TC will aid in triggering puberty in hypogonadal males and can help to restore lost libido and sexual function in adults.
Testosterone cypionate is one of a number of testosterone derivatives, a testosterone ester. Test esters have been altered slightly by the addition of a single reactive ester group to the molecule. Depo-Testosterone is, therefore, more soluble in fats, so when given as an intramuscular injection it remains in the tissue and is slowly released over a number of days.
Yes. Testosterone cypionate is available as the brand-name drug Depo-Testosterone. It’s also available as a generic drug, which may not be as strong as the branded version. The reason for this? Generic drugs usually cost less than their counterparts and are often manufactured by different companies that cannot produce all strengths because of patent rights.
Testosterone cypionate is only taken by directions from your physician. Side effects can be common and can range from mild to severe [7].
There are a number of mild adverse reactions that may occur when taking a testosterone derivative:
It should be noted that if you feel sudden onset chest pain you should always inform your physician. It may just be a symptom of androgen therapy but also as an indicator of a more serious, underlying condition.
There are also a number of more serious adverse reactions to depo testosterone therapy;
Drugs often have interaction issues with other medications you may be taking. Here is a detailed checklist to help you [11]:
Testosterone cypionate is available as an injectable solution. You can take it either as an intramuscular shot or as a subcutaneous injection.
Typical drug regimes are between 50 mg ml and 400 mg ml every two weeks. The maximum recommended dose is 400 mg ml as an intramuscular injection every two weeks. The dosage you take will depend on t your age, however, it is safe for pediatric patients above 12 years of age [12].
TC is used when serum testosterone levels are reduced, causing a specific or a set of low-t-related problems. The bi-weekly injections are to either boost or replace the body’s missing testosterone.
Your doctor will demonstrate how to inject yourself. Once you are confident you will be able to do this yourself.
Testosterone injections are given usually as an intramuscular shot, meaning you inject it directly into muscle mass and not into the blood. Typically the buttocks or thighs are the most common injection sites.
It can also be given subcutaneously, meaning under the skin. This is less common and your doctor will advise you which is best.
Most testosterone treatments are bi-weekly shots. However, it will depend on the reason you’re taking the drug.
Your doctor will assess your condition by looking at your serum testosterone concentration and work out which is the best treatment plan for you.
As the testosterone treatment progresses, your doctor will monitor your testosterone blood levels and, after discussion, may alter your treatment schedule. This is normal and not a sign that there is anything wrong.
It is recommended that you store TC away from bright light and at room temperature, between 68 and 77 degrees Fahrenheit (20 and 25 celsius).
Like most prescription drugs Depo-Testosterone or TC requires you to be careful about how and where you store the drug. If you do not follow these guidelines the drug may degrade and lose efficacy.
There are other ways to help boost low testosterone levels—some are prescription-only drugs and some are over-the-counter remedies that you can buy.
This is marketed as an over-the-counter testosterone booster. Testogen is available in either pill or liquid form. It is labeled as an ‘All Natural’ testosterone booster/supplement with a mix of 11 ingredients that all aim to boost your level of testosterone. See here for our Testogen review.
Prime Male is marketed as a ‘Natural Testosterone Booster’. Being a mix of 12 compounds, it’s similar to Testogen, but is only available in pill form.
As with Testogen, it is widely available over the counter and online. See here for our Prime Male review.
TestRX is marketed as a dietary supplement and contains a range of natural ingredients that claim to boost or maintain your testosterone.
As with the other three, it is aimed at middle-aged men who feel that they are lacking a little ‘zip’ in their life. See here for our TestRX review.
There is a lot of information out there so we have answered the most common questions people have asked.
TC is widely available with a prescription. You can find it in health food stores as well as a wide range of internet outlets.
Testosterone Cypionate is a Schedule III drug and as such, is only available on prescription.
The average cost for two vials of 200 mg ml is $50 online. As always prices may vary and shopping around for better deals, buying in bulk or looking for special offers may get you a lower price.
An intramuscular testosterone shot is designed to be a slow-release drug, and it may be three to six weeks or more before you see the results. Any form of androgen therapy is designed to have an effect over time. The result is not immediate like you would expect from a pain killer.
Your doctor will monitor your serum testosterone concentrations over time and advise you accordingly.
The short answer is yes. Anabolic steroids like TC have a range of effects on the body. One of which is adding muscle.
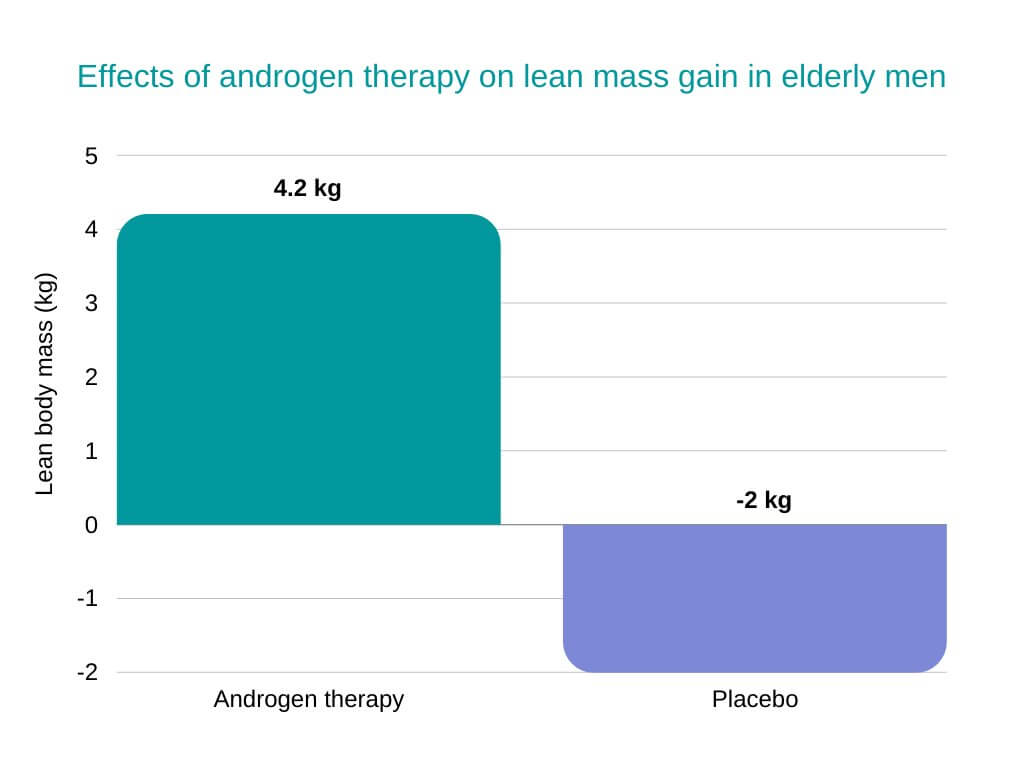
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4312307/
The short answer is again, NO, at least not legally. TC is a prescription drug and can’t be legally used recreationally.
TC increases the rate of protein synthesis, which can lead to an increase in muscle mass. For this to be effective you would need to alter your lifestyle, diet, and exercise regime.
Having low testosterone levels can cause a number of serious health issues for you. It is important to see a doctor and follow his or her advice. With correct monitoring, the treatment is safe and effective, so do not worry about any scare stories you may have heard of.
You may be taking testosterone for a protracted period of time. Adjusting to weekly or biweekly injections may seem difficult but it will soon become second nature.
Good luck with your treatment and, of course, get well soon.